Bleeding Gums Cancer: Must Know Signs and Symptoms
Contents
- What are the Symptoms and Signs of Bleeding Gum Cancer?
- Is Bleeding Gums a Sign of Cancer?
- How Often Do Bleeding Gums Represent Cancer?
- What Are the Treatment Options for Bleeding Gum Cancer?
- Conclusion
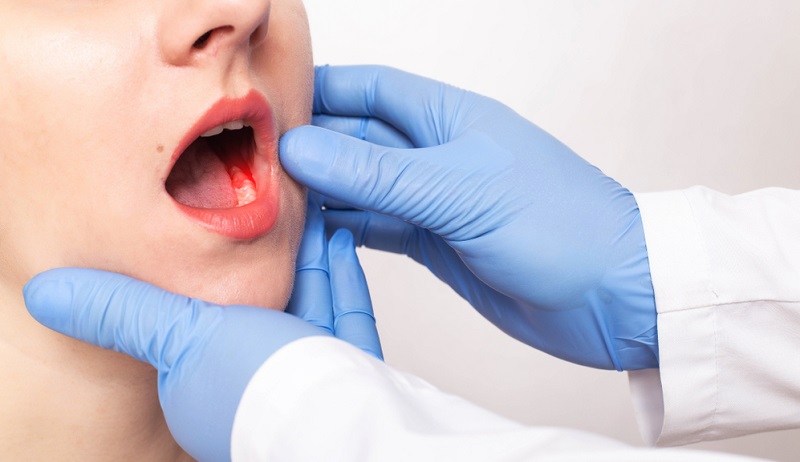
Bleeding gums can be a common and often overlooked issue, especially when it happens during brushing or flossing. However, persistent bleeding gums can sometimes signal a more serious condition, such as gum cancer.
In this article, we'll explore the signs and symptoms of bleeding gum cancer in a friendly and approachable way. You'll also discover the available treatment options to help you maintain your oral health and peace of mind.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Bleeding Gum Cancer?
1. Continued Bleeding
Persistent and unexplained gum bleeding is one of the key indicators of bleeding gum cancer. It is highly imperative to pay attention in such cases.
If your gums bleed frequently for no obvious reason, such as injury or forceful brushing, it needs inspection and should be handled carefully and should be evaluated by your dentist or healthcare practitioner.
2. Changes in Gum Appearance
Bleeding gum cancer can produce significant changes in the appearance of your gum tissue in some circumstances. Look out for any abnormal changes, such as a lump, swelling, or gum discolouration.
These changes can also occur due to other ailments, but it is advised to have them checked out by a dental or medical specialist to rule out any major underlying disorders.
3. Changes in Gum Appearance
In some cases, bleeding gum cancer may cause noticeable changes in the appearance of your gum tissue. Keep an eye out for any unusual changes, such as a lump, swelling, or discolouration of the gums.
There are high chances that these changes can also be caused by other conditions, but having them examined by a dental or medical professional to rule out any serious underlying issues is always a better way to go about it.
4. Loose Teeth or Teeth Shifting
As bleeding gums cancer advances, it can compromise the supporting structures of your teeth, resulting in loose teeth or a shift in the alignment of your teeth.
If you observe any changes in the stability or location of your teeth, you should seek expert help right away. Remember that early detection and action can make a big difference in treatment success.
5. Pain and Discomfort
While not everyone with bleeding gums cancer has pain, it is important to mention that some people may experience discomfort or sensitivity in their gums or mouth.
This soreness may linger even after basic oral care procedures, or it may worsen with time. If you experience continued dental discomfort, talk to your doctor or dentist to figure out what's causing it.
6. Eating or Speaking Difficulties
You may find it difficult to chew or speak comfortably if you have advanced bleeding gums cancer. One reason for this might be related to tumour-induced gum inflammation, ulceration, or alterations in the oral cavity.
If you are having a tough time dealing with your daily activities, you must get professional help to determine the underlying problem and explore appropriate treatment options.
Is Bleeding Gums a Sign of Cancer?
Gum cancer is typically anything that grows from the surface of the gums. It is usually in a clump and might be red or white. It could potentially haemorrhage.
Gingivitis, on the other hand, is a mild infection of the gum line caused by bacteria that naturally exist there and produce irritation. When your gums are touched or flossed, they may become irritated and swollen, or painful. It is extremely frequent and is caused by inadequate dental hygiene.
Periodontitis is a more severe form of gum disease. It's a severe kind of gingivitis that only appears after a long period of gingivitis. If left untreated, it might progress to further tooth and jawbone issues. However, most cases of gum disease should not result in anything serious.
Gum cancer can be identified by patches or irregular growths on the gums. These growths and patches are red and white in colour. Erythroleukoplakia (red and white patches or growths) and leukoplakia (just white) or erythroplakia (just red) are their scientific names. Erythroleukoplakia and erythroplakia are more likely to be malignant than leukoplakia.
Gum cancer and gum disease are sometimes confused, which is why it's critical to have regular dental treatments. Cancers of this sort can spread swiftly. For the greatest potential outcome, early detection is critical.
How Often Do Bleeding Gums Represent Cancer?
- Bleeding gums are usually linked to various dental and oral health issues, but they rarely indicate oral cancer on their own. The most common cause is gum disease, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, often due to poor oral hygiene. Other causes include brushing too hard, using a hard-bristled toothbrush, and certain medications.
- While it's rare, bleeding gums can sometimes be a symptom of oral cancer. However, this is far less common compared to other causes.
- Gum damage from brushing or eating hard foods is more likely if you have plaque and tartar buildup. Even mild gum disease can lead to irritation, making gums prone to cuts and tears.
- Bleeding gums can also be an early sign of leukaemia, often accompanied by other mouth-related symptoms. Diagnosing these conditions may involve biopsies and imaging tests. If oral cancer is detected, you'll be referred to a specialist for treatment.
- It's important to note that while bleeding gums are rarely a sign of oral cancer, they shouldn't be ignored. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene, and professional advice for any concerns are crucial for early diagnosis and treatment of potential problems.
What Are the Treatment Options for Bleeding Gum Cancer?
Bleeding gum cancer is usually treated using a combination of different approaches to give the best chance of recovery.
The exact treatment plan depends on factors like the stage of cancer, tumour size, and overall health of the patient.
Here are some common treatment options:
1. Surgery:
Surgery is often the main treatment for bleeding gum cancer. The goal is to remove the tumour and some healthy tissue around it to ensure all the cancer cells are gone.
The extent of the surgery depends on the size and stage of the tumour. Sometimes, parts of the gums, lymph nodes, or even the jawbone may need to be removed. After surgery, reconstructive techniques can be used to restore function and appearance.
2. Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, like X-rays, to target and kill cancer cells. It is often used after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells or as the main treatment if surgery is not possible.
External beam radiation therapy is commonly used, where the radiation is delivered from a machine outside the body. Another type, called brachytherapy, involves placing radioactive sources near the tumour.
3. Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy involves using strong medications to kill cancer cells or slow down their growth. It is often used for bleeding gum cancer that has spread or if the tumour is large or aggressive.
Chemotherapy can be taken as pills or given through an intravenous infusion. It may be used before surgery to shrink the tumour or after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
4. Targeted Therapy:
Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target certain abnormalities or proteins in cancer cells. These medications interfere with the growth and spread of cancer cells while causing less harm to healthy cells.
Targeted therapy may be used along with other treatments or on its own, depending on the specific characteristics of the tumour.
5. Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that boosts your body's immune system to fight cancer. It helps the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
Immunotherapy may be an option for bleeding gum cancer, especially when other treatments have not been successful.
6. Palliative Care:
In cases where bleeding gum cancer is advanced or cannot be cured, palliative care becomes important. Palliative care focuses on managing symptoms, providing pain relief, and addressing emotional and psychological needs to improve the patient's quality of life.
Remember, each person's treatment plan is unique, so it's essential to work closely with a healthcare team to determine the best approach for treating bleeding gum cancer.
Conclusion
Remember that the above-mentioned signs and symptoms are potential markers of bleeding gums cancer, but they can also be caused by other illnesses.
It is critical not to leap to conclusions and instead seek advice from knowledgeable dental or medical professionals.
Regular dental exams and proper oral hygiene habits can also aid in the detection of early signs of gum disease or other oral health disorders.
You're taking an active role in your dental health and general well-being by remaining informed and proactive.