Gum Boils: Causes, Treatment & How to Soothe Your Pain
Contents
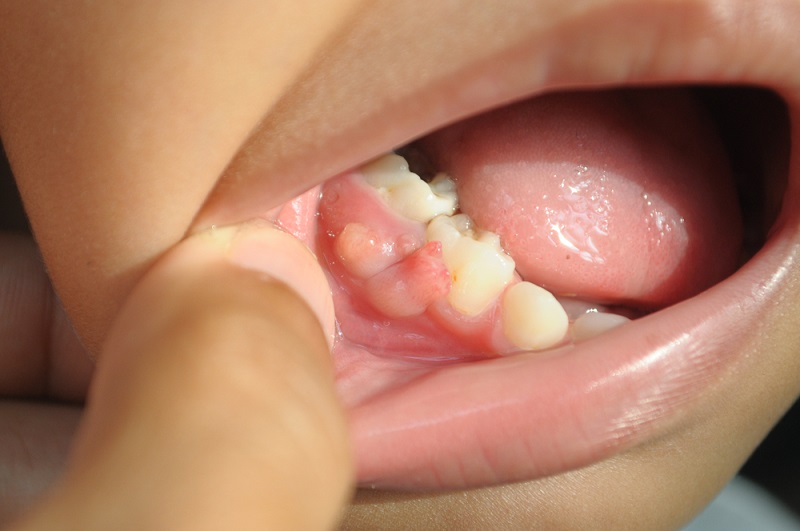
A gum boil is a type of abscess that develops on the gums. They are visible as swollen lumps on the gums.
The main cause of a gum boil is bacteria, which causes infection beneath the surface of the gum due to plaque, food particles, or tooth decay. A gum boil is only seldom a sign of oral cancer.
The gum boil is classified into one of three forms based on its location:
Gingival abscess: an infection of the gums
At the tooth's root: periapical abscess
Periodontal abscess in the tooth-supporting tissues
What Are the Causes of Gum Boils?
The most prevalent causes of dental abscesses of the teeth or gums include poor dental hygiene, tooth decay, and trauma. A gingival abscess can be caused by hard brushing.
Anything that destroys the protective enamel of a tooth can allow bacteria to enter and cause an infection and abscess.
The infection strains the inner tissues of the tooth, resulting in excruciating pain. It then makes its way into the root canal and into the jaw, causing a lump on the gums.
Gum boils can also be caused by the following factors:
Teeth that have partially erupted
Some medical conditions
Teeth clenching
Irritating chemicals
Dentures that are not properly fitted
Immunosuppression
Cancer of the oral cavity
How to Deal with a Gum Boil?
To avoid problems, gum boils require professional evaluation and treatment. Some home cures, on the other hand, may assist in relieving pain and discomfort.
Home Treatments
1. Mouthwash with Saltwater
Some dangerous oral germs may be killed by salt rinses. They also get rid of any loose material and help to minimise inflammation and swelling.
According to research, salt water rinsing benefits gum health and enhances oral wound healing.
Around 2% salt is the most effective concentration. 1 teaspoon of salt in a cup of water equals a salt rinse.5
Before spitting it out, swish the liquid around your mouth for around 30 seconds. Rep many times every day.
2. Mouthwash with Hydrogen Peroxide
Antibacterial characteristics are possessed by hydrogen peroxide. It may alleviate the discomfort and inflammation caused by gum disease, the leading cause of tooth abscesses.
Researchers discovered that individuals utilising hydrogen peroxide for gum disease had fewer symptoms than the control group in a 2017 study.
Make mouthwash by combining one part hydrogen peroxide and two parts water. Twice a day, swish the liquid around your mouth.
3. Paste of Turmeric
Turmeric's primary element, curcumin, is a natural anti-inflammatory. Brush as usual after mixing a little amount of turmeric into regular toothpaste.
Turmeric mouthwash may also aid in the removal of plaque and bacteria. They have been demonstrated to decrease inflammation and aid in the prevention of gum disease.
Other research suggests that turmeric can help heal periodontal disease and lessen dental pain.
4. Aromatherapy Oils
The natural qualities of essential oils may reduce oral microorganisms. According to research, peppermint oil can help fight harmful mouth bacteria. It may also help with foul breath.
Eugenol is found in clove oil. This natural compound possesses antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anaesthetic effects. As a result, it may aid in the treatment of dental decay.
Cinnamon oil, too, has antibacterial and antifungal properties. According to research, it may help to prevent bacterial infections in the mouth.
To use essential oils for oral health, follow these steps:
- 1 drop can be mixed into ordinary toothpaste or mouthwash.
- 1 drop of essential oil and 1/4 cup water are combined to make a mouth rinse.
- 1 drop essential oil and 1 tablespoon carrier oil, such as coconut oil, combined
- In your mouth, swish the liquid around.
- Spit into the sink (do not consume any).
Professional Treatments
The first stage of treatment focuses on symptom relief and infection prevention. A dentist may then recommend additional treatment to prevent recurrence.
1. Cleaning and Drainage
Your dentist will drain the abscess and remove the pus through a gum incision. They will next clean the periodontal pocket and remove dead tissue and bacteria with dental tools.
Finally, an antiseptic rinse will help destroy any lingering bacteria.
By draining and cleansing the gum boil, your immune system can control the infection.
2. Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed by the dentist to kill the bacteria that is causing the infection. If the abscess grows beneath the gum line, draining it may be impossible. Antibiotics can be useful in certain situations.
If the infection has spread or the person has a weaker immune system, they may additionally recommend antibiotics.
The first-line antibiotic is amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid. Clindamycin is an alternative to penicillin for persons who are allergic to it.
3. Additional Therapy
If you have a periapical abscess in the root of a tooth, the infection may require a root canal.
This entails cleansing and sanitizing the inflammatory, diseased tissue inside the tooth. The space is then filled with a filler.
If a dentist believes that root canal therapy will not preserve the tooth, he or she may propose tooth extraction.
Gum infections can harm the underlying jawbone in extreme cases. The dead portions may then need to be removed by the dentist.
How to Prevent a Gum Boil?
The easiest approach to avoid gum boils is to maintain adequate oral hygiene.
This includes the following:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day is recommended.
- Flossing every day
- Visiting the dentist regularly Most people require dental checkups every six months.
- If you have dental problems, you may need to come in more frequently. Contact your dentist as soon as you see any signs of illness or irritation.
- Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease. It also reduces the success of treatment. As a result, stopping smoking may aid in the prevention of gum boils.
- Another risk factor for gum disease and boils is diabetes. High blood sugar levels increase the amount of glucose in the saliva, creating ideal circumstances for bacterial development.
- Blood sugar control is critical. If you have dental symptoms, see your dentist as soon as possible.
Conclusion
If you get a gum boil, see your dentist. Treatment will be required to prevent the infection from spreading and to alleviate symptoms.
The abscess may be drained, antibiotics taken, or a root canal performed.
Brushing and flossing daily, seeing your dentist for regular exams, and quitting smoking can all help avoid gum boils.
FAQs
What is a Gum Boil?
Gum boils, also known as dental abscesses or gum abscesses, are painful, swollen bumps or lumps that occur on the gum tissue.
It is usually filled with pus and indicates a gum or tooth infection.
Are Gum Boils Painful?
Yes, gum boils can be uncomfortable. They can cause pain, throbbing, and discomfort. The pain is frequently accompanied by swelling, redness, and, in rare cases, fever.
Seeking immediate dental care is critical for relieving discomfort and addressing the underlying issue.
Can Gum Boil Heal Its Own?
Gum boils do not usually heal on their own. They are the result of an infection, and if not treated properly, the condition may worsen.
It is critical to see a dentist for proper care, which may include emptying the abscess and prescription antibiotics.
What Causes Gum Boils?
Bacterial infections are the most common cause of gum boils. These infections can be caused by a variety of oral disorders, including untreated cavities, gum disease, or dental trauma.
When bacteria invade the pulp of the gums or teeth, an abscess can occur.
Can Gum Boils Spread?
Yes, if left untreated, Gum Boils can spread. The infection can spread into the surrounding tissues, creating more serious health problems.
To prevent the infection from spreading, get professional dental care as soon as you discover symptoms.
Can Gum Boil Cause Cancer?
Gum Boils are not directly associated with cancer. Chronic infections and long-term inflammation in the oral cavity, on the other hand, have been linked to an increased risk of some malignancies, including oral cancer.
To limit the risk of problems and maintain dental health, gum boils must be addressed and treated as soon as possible.
Regular dental check-ups can help avoid serious oral health problems, including cancer.