Contents
- What are Cavities in Children?
- Causes of Cavities in Kids
- Signs and Symptoms of Cavities in Kids
- 1. White spots or discolouration on the teeth:
- 2. Brown or black spots on the teeth:
- 3. Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods:
- 4. Pain or discomfort when chewing:
- 5. Visible holes in the teeth:
- Diagnosis for Cavities in Kids
- Treatments for Cavities in Kids
- Prevention Tips for Avoiding Cavities in Kids
- Questions to Ask Your Pediatrician or Dentist
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What causes cavities in kids?
- Can kids' cavities be reversed?
- How do kids' teeth get cavities?
- How many kids are having untreated cavities?
- How many kids have cavities in their teeth?
- How to avoid cavities in a 6-year-old kid's teeth?
- How to explain a cavity to a kid?
- How to get rid of dental cavities in kids?
- How to remove cavities for kids?
- How to remove front teeth cavities in kids?
- How to treat cavities in kids?
As a parent, keeping your child's teeth healthy is one of the most important things you can do for their overall well-being.
Cavities are common among children and can cause discomfort, pain, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
But how do you spot cavities in your child before they become a bigger problem?
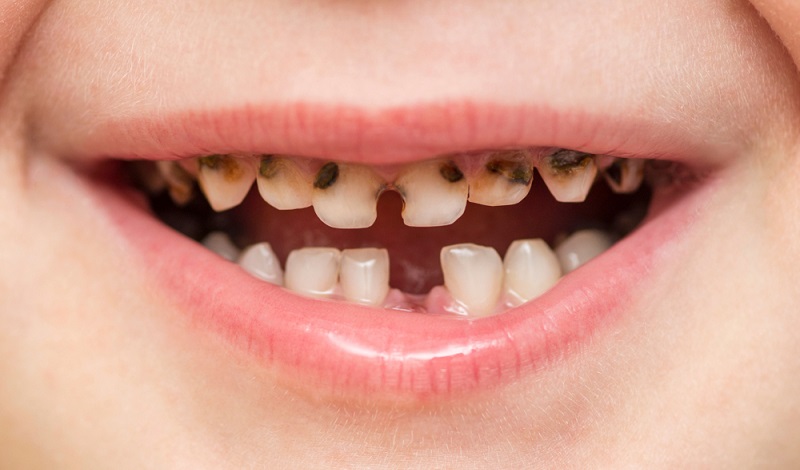
In this blog post, we'll explore the signs and symptoms to look out for so that you can catch any potential cavities early on and keep your child's smile shining bright!
What are Cavities in Children?
Cavities are small holes in the teeth that can be caused by bacteria. When bacteria build up on the teeth, they can create an acidic environment that will eat away at the tooth enamel and cause cavities.
Children are especially susceptible to cavities because their teeth are still developing and they may not have good oral hygiene habits yet.
Causes of Cavities in Kids
- Cavities form when a buildup of dental plaque eats away at tooth enamel, creating a hole.
- Plaque is a sticky substance formed on teeth as a result of bacteria in the mouth reacting with food, acid, and saliva.
- Cavities commonly arise when children do not brush their teeth properly because regular brushing and flossing help prevent plaque formation.
- Children should brush their teeth for at least 2 minutes twice a day. Some children, however, only brush their teeth once a day. Worse, they entirely disregard brushing.
- Children cannot brush well on their own until they are around 6 years old.
- It is critical that an adult washes a child's teeth or oversees their brushing until they are mature enough to do so properly.
- Furthermore, some youngsters may not floss their teeth or floss incorrectly.
- Cavities can also form if plaque and food particles are not cleaned from between the teeth.
- Flossing can be difficult for children, therefore parents should assist them with this vital task.
- Also, keep in mind that good tooth hygiene includes frequent dental visits.
- You should schedule dental appointments for your children on the same schedule as adults do.
- Because infant teeth normally erupt about 6 months of age, book your child's first dental visit soon after their first tooth appears.
- Of course, poor oral hygiene isn't the only cause of cavities; food plays a role as well.
- If your child consumes a lot of sugar, he or she is more likely to develop dental decay.
Signs and Symptoms of Cavities in Kids
Cavity signs and symptoms vary from kid to child, but frequent signs include:
- Spots of white on the teeth.
- The development of a light brown colour on the teeth.
- Discoloration of the teeth.
- A gap in the tooth.
- Sweet or cold meal reactions.
If your child has visible evidence of a cavity, they should consult a dentist. Your dentist will use a filling, commonly known as a restoration, to fix their cavities.
Restorations are classified into two types: direct and indirect. To fill the cavity holes, direct restorations require only one visit.
Indirect restorations need two visits and entail tooth repairs using a customised material.
If your kid exhibits any of the following signs, seek emergency medical attention:
- Pain or swelling has become more severe.
- Fever and other infection symptoms.
- Pus draining from the tooth causing difficulty swallowing or chewing.
Untreated cavities and dental decay can result in life-threatening infections with long-term consequences.
Diagnosis for Cavities in Kids
Steps for Diagnosing Cavities in Kids:
Medical History Review:
The dentist will ask about your child’s dental hygiene habits and any existing medical conditions that may increase their risk of cavities.
Dental Examination:
A thorough examination of the child’s teeth and gums is conducted to check for visible signs of tooth decay, discoloration, or damage.
X-Rays for Accurate Diagnosis:
If cavities are suspected, the dentist may take X-rays to detect decay that isn’t visible to the naked eye. X-rays can reveal small cavities between teeth and beneath the surface.
Determining Treatment Options:
Once cavities are confirmed, the dentist will discuss the best treatment options, which could range from fluoride treatments and fillings to more extensive procedures depending on the severity of decay.
Treatments for Cavities in Kids
Common Treatment Options for Cavities in Kids:
Dental Fillings:
The most common treatment for cavities in kids is a dental filling, suitable for both baby (primary) and permanent teeth.
During the procedure, the dentist removes the decayed portion of the tooth and fills the cavity with a white composite or metal material.
Filling a cavity in a baby tooth helps preserve the tooth, preventing early loss which can lead to alignment issues when permanent teeth emerge.
Dental Crowns:
In cases of extensive tooth decay, a dental crown may be necessary to restore the tooth's shape and function.
Crowns are typically recommended when there isn’t enough healthy tooth structure left to support a filling.
Tooth Extraction:
If a baby's tooth is severely damaged or infected, extraction may be required.
After extraction, a space maintainer is used to keep the gap open, ensuring proper alignment of incoming permanent teeth.
Additional Treatment Considerations:
Sedation Options for Young Children:
Dental procedures can be challenging for small children. Dentists may use nitrous oxide (laughing gas) to help them relax during treatment.
In some cases, oral sedation may be given before the procedure to help calm the child.
Local anesthesia is still necessary to numb the gums, but sedation helps make the process smoother and less stressful for both the child and the dentist.
Staggered Appointments:
If multiple cavities need treatment, the dentist may suggest spacing out appointments to make each visit more manageable for the child.
Importance of Timely Treatment:
Preserving baby teeth is crucial for proper chewing, speaking, and maintaining the space needed for permanent teeth to grow correctly. Early intervention can prevent more serious dental problems down the road.
Prevention Tips for Avoiding Cavities in Kids
Cavities are one of the most common childhood diseases, but they are also preventable.
Here are some tips for preventing cavities in your child:
1. Encourage your child to brush their teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
2. Help them floss once a day.
3. Limit sugary drinks and snacks.
4. Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings.
Questions to Ask Your Pediatrician or Dentist
It's important to be proactive about your child's dental health and spot any potential problems early on.
Here are some questions to ask your paediatrician or dentist about cavities:
- What are the signs and symptoms of a cavity?
- How can I tell if my child has a cavity?
- What should I do if I think my child has a cavity?
- How can I prevent cavities in my child?
Conclusion
Spotting cavities in your child's teeth can be difficult, but knowing the signs and symptoms to look out for makes it easier.
It is important to ensure children brush their teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and have regular dental checkups.
So that any cavities can be treated as soon as possible. Following these tips can help keep your child’s smile healthy and happy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes cavities in kids?
Cavities in kids are caused by the buildup of bacteria on teeth, which produce acid that attacks the enamel and causes decay.
This is often due to poor oral hygiene, such as not brushing or flossing regularly, as well as consuming sugary or acidic foods and drinks.
Can kids' cavities be reversed?
Early-stage cavities can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and fluoride treatment.
However, once a cavity has progressed to a certain point, it cannot be reversed and requires a filling or other dental treatment.
How do kids' teeth get cavities?
Kids' teeth can get cavities from a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene, sugary or acidic foods and drinks, frequent snacking, and a lack of fluoride.
How many kids are having untreated cavities?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 1 in 4 children aged 2-11 years old in the United States have untreated cavities.
How many kids have cavities in their teeth?
According to the CDC, approximately 45% of children aged 2-19 years old in the United States have cavities in their primary (baby) teeth, and 68% have cavities in their permanent teeth.
How to avoid cavities in a 6-year-old kid's teeth?
To avoid cavities in a 6-year-old's teeth, it's important to encourage good oral hygiene habits such as brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks, and visiting the dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
How to explain a cavity to a kid?
A cavity is a small hole that forms in a tooth when bacteria and acid break down the enamel.
It's important to explain to kids that cavities can be prevented with good oral hygiene and a healthy diet.
How to get rid of dental cavities in kids?
Getting rid of a dental cavity in a child typically involves removing the decayed portion of the tooth and filling the cavity with a filling material.
How to remove cavities for kids?
Cavities are typically removed using a dental drill or laser to remove the decayed portion of the tooth. The cavity is then filled with a filling material.
How to remove front teeth cavities in kids?
The treatment for a front teeth cavity in a child will depend on the severity of the decay.
If the cavity is minor, it may be possible to fill the cavity. In more severe cases, the tooth may need to be extracted or a crown may need to be placed.
How to treat cavities in kids?
Treatment for a cavity in a child typically involves removing the decayed portion of the tooth and filling the cavity with a filling material.
In more severe cases, a crown or root canal may be necessary. It's important to consult with a dentist to determine the best course of treatment for your child's cavity.