Is Your Chest Pain Caused by Acid Reflux: Know the Signs and Solutions
Contents
- Understanding Acid Reflux and its Symptoms:
- What Causes Acid Reflux Chest Pain?
- Differentiating Acid Reflux Chest Pain from Other Types of Chest Pain?
- The Various Areas Where Acid Reflux Pain Occurs:
- GERD Chest Pain: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment:
- How to Relieve Acid Reflux Chest Pain and Prevent Its Recurrence:
- 1. Avoiding Trigger Foods:
- 2. Eating smaller meals:
- 3. Elevating the Head of the Bed:
- Quitting Smoking:
- Prescription Medications:
- Conclusion:
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Does GERD cause left side chest pain?
- 2. Does the chest hurt with acid reflux?
- 3. Where do chest pains from acid reflux occur?
- 4. How can GERD pain be eliminated?
- 5. How to prevent acid reflux?
- 6. Can acid reflux chest pain last for days?
- 7. Can acid reflux chest pain come and go?
- 8. Can acid reflux chest pain last for months?
- 9. How long does acid reflux chest pain last?
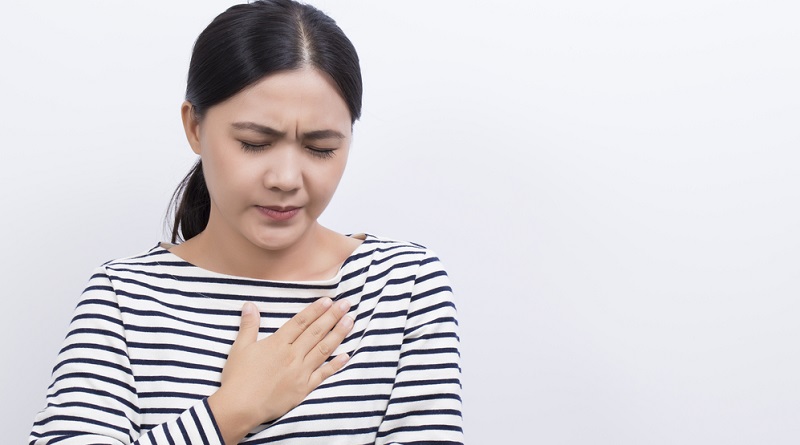

Acid reflux is a common digestive issue where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation. One of its most troubling symptoms is chest pain, which can often feel alarmingly similar to a heart attack.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for acid reflux chest pain, helping you better understand this discomfort and how to manage it effectively.
Understanding Acid Reflux and its Symptoms:
When the lower oesophagal sphincter (LES), a muscle that serves as a valve between the oesophagus and the stomach, isn't working properly, acid reflux develops.
Heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest and throat that occurs when the LES is weak or relaxes improperly, allowing stomach acid to flow back up into the oesophagus.
- Regurgitation
- Bloating
- Nausea, and
- Difficulty Swallowing.
What Causes Acid Reflux Chest Pain?
Acid reflux chest pain occurs primarily due to irritation of the esophagus by stomach acid. However, several factors can contribute to this discomfort:
1. Hiatal Hernia
A condition where part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest, making acid reflux more likely.
2. Obesity
Excess body weight puts pressure on the stomach, forcing acid back into the esophagus.
3. Large Meals or Lying Down After Eating
Eating large portions or reclining immediately after a meal can trigger acid reflux by increasing pressure on the stomach.
4. Smoking
Smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) and boosts stomach acid production, both of which increase the risk of acid reflux.
5. Medications
Certain drugs, like aspirin and ibuprofen, can irritate the esophagus and make acid reflux chest pain more likely.
Differentiating Acid Reflux Chest Pain from Other Types of Chest Pain?
It can be challenging to distinguish between chest pain from acid reflux and other types of chest pain, including the chest pain experienced during a heart attack.
However, there are specific characteristics that set acid reflux chest pain apart from other kinds of chest discomfort.
Usually, acid reflux chest pain:
- Occurs after a meal or at night
- Is accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest or throat
- May be relieved by antacids
- Does not radiate to the arms or jaw
If you experience chest pain that lasts for more than a few minutes and is accompanied by shortness of breath, dizziness, or sweating, seek medical attention immediately.
The Various Areas Where Acid Reflux Pain Occurs:
Acid reflux chest pain can occur in different areas of the chest, depending on the severity and location of the irritation in the oesophagus.
The most common areas where this pain occurs are as follows:
The centre of the chest, which can mimic the symptoms of a heart attack
The upper chest, which can cause discomfort and a burning sensation in the throat
The lower chest, which can cause pain in the stomach area
GERD Chest Pain: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment:
A severe form of acid reflux known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can result in chronic chest discomfort and other symptoms.
Acid reflux and GERD chest pain symptoms are similar, however, GERD chest pain symptoms can be more severe and long-lasting.
Your doctor may order several tests to identify GERD if you have persistent or severe chest discomfort, including:
1. Upper Endoscopy:
A procedure in which the oesophagus is examined for inflammation and damage using a flexible tube with a camera.
2. Oesophageal pH Monitoring-
A test that gauges how much acid is present in the oesophagus over a day.
In most cases, a combination of lifestyle changes and medications is used to manage GERD chest discomfort.
Losing weight, avoiding trigger foods, and raising the head of the bed are a few examples of lifestyle changes.
Antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 blockers are a few possible medications.
How to Relieve Acid Reflux Chest Pain and Prevent Its Recurrence:
1. Avoid Trigger Foods
Certain foods, especially spicy, fatty, or acidic ones, can exacerbate acid reflux and lead to chest pain. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of your symptoms. Common culprits include tomatoes, citrus fruits, chocolate, and caffeine.
2. Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals
Large meals put extra pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Opt for smaller, more frequent meals to help minimize this pressure and reduce the likelihood of experiencing chest pain.
3. Elevate the Head of Your Bed
Sleeping with the head of your bed raised can help prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus while you sleep. This elevation reduces nighttime reflux and alleviates related chest pain. Consider using a wedge pillow or adjustable bed for optimal results.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking weakens the LES and increases stomach acid production, both of which contribute to acid reflux and chest pain. Quitting smoking not only improves your overall health but also helps reduce the risk of acid reflux symptoms.
5. Use Prescription Medications
Medications such as antacids and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are often prescribed to manage acid reflux. These medications work by reducing stomach acid production and neutralizing excess acid, providing relief from chest pain and preventing recurrence.
Conclusion:
Acid reflux chest discomfort is a typical symptom that can be severe and resemble heart attack symptoms.
People can better manage their symptoms and avoid them returning by being aware of the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for acid reflux chest pain.
People with acid reflux chest discomfort can find relief and enhance their quality of life by changing their lifestyles, such as avoiding GERD trigger foods, eating smaller meals, raising the head of the bed, stopping smoking, and taking medications as directed.
To rule out any underlying medical issues, get medical assistance right away if you have regular or severe chest pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does GERD cause left-side chest pain?
Yes, left-side chest pain can result from GERD. Acid reflux may irritate the oesophagus and cause inflammation or spasms, which would explain the pain.
But it's crucial to keep in mind that left-side chest discomfort can also be a sign of other illnesses, such as heart attack, so it's crucial to get medical help if you have chest pain.
2. Does the chest hurt with acid reflux?
Yes, acid reflux can cause chest pain. Typically, the discomfort is described as a scorching sensation that may extend up to the throat and neck.
Other symptoms including nausea, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing may also be present in addition to the chest pain.
3. Where do chest pains from acid reflux occur?
The chest, throat, and stomach are just a few of the places where acid reflux chest discomfort can develop.
The left side or the centre of the chest may be the location of the pain. Additionally, the neck, throat, and back may be affected.
4. How can GERD pain be eliminated?
Medication and lifestyle changes are frequently used to treat GERD pain. Losing weight, elevating the head of the bed, and avoiding trigger foods are a few examples of lifestyle changes.
Antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 blockers are a few possible medications.
5. How to prevent acid reflux?
To prevent acid reflux, you can change your lifestyle by avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, avoiding lying down shortly after eating, and, if necessary, losing weight.
You can also take medications as prescribed by your doctor to lower the amount of stomach acid.
6. Can acid reflux chest pain last for days?
Chest pain can last for days if acid reflux is not treated. It is important to remember that chest pain can also be an indication of other medical conditions, such as a heart attack, so if it lasts for a long time, seek medical attention immediately.
7. Can acid reflux chest pain come and go?
Yes, it can happen. The discomfort may come and go and be brought on by particular food or activities.
However, it is important to keep in mind that chest pain can also be a symptom of other ailments, such as a heart attack, making it imperative to seek medical attention in these circumstances.
8. Can acid reflux chest pain last for months?
Yes, if untreated, this chest pain could last for months. However, keep in mind that soreness in the chest may also be a sign of other medical conditions, such as a heart attack, so please seek medical care if needed.
9. How long does acid reflux chest pain last?
The severity of the issue and how well the treatment is working will determine how long acid reflux chest discomfort lasts.
In moderate cases, acid reflux chest pain may only last a few minutes, whereas severe ones may linger for several hours or days.