Contents
- What is an Abscess?
- Causes of Abscess
- Types of Abscess in Your Mouth
- 1. Gingival Abscess:
- 2. Periapical Abscess
- 3. Periodontal Abscess:
- 4. Tonsil Abscess:
- 5. Quinsy Abscess:
- 6. Retropharyngeal Abscess
- Symptoms of Abscess
- Risk Factors of Mouth Abscess
- Prevention of Mouth Abscess
- What is the Best Way to Treat an Abscess?
- Can Abscess Heal on Its Own?
- Conclusion
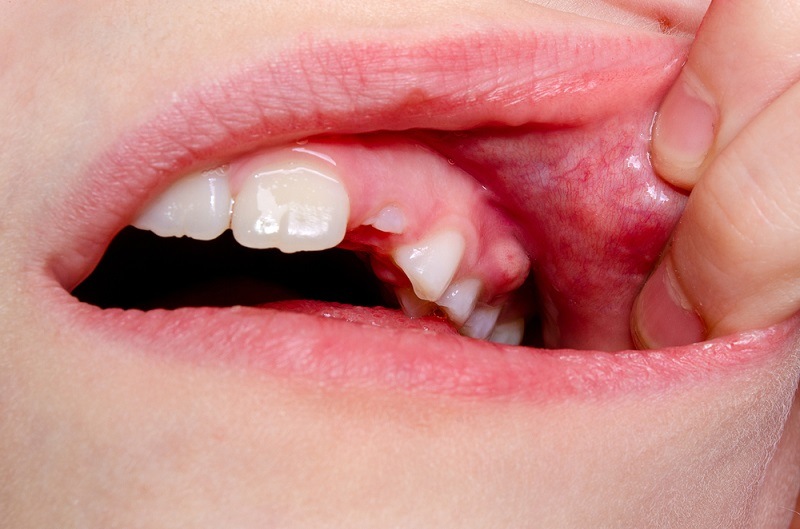
What is an Abscess?
An abscess is a pus-filled pocket caused by a bacterial infection in your gums. An abscess typically resembles a red, swollen lump, boil, or pimple.
The infection affects the afflicted tooth but can also spread to the adjacent bone and neighbouring teeth.
Abscesses can form in various locations around a tooth for various causes.
Causes of Abscess
Abscesses can be caused by three types of tooth infections:
- Gingival infection occurs in the gums. It normally has little effect on your teeth or supporting structures. 6442, 2
- A periapical abscess is an infection that develops near the tip of your tooth root.
- Bacteria can enter your tooth and spread to the pulp if it is decaying or cracked. (The pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels, is the interior component of the tooth.)
- When germs infiltrate the pulp, infection can move to the tip of your tooth's root and subsequently to the surrounding bone, resulting in an abscess.
- Periodontal disease begins in the bones and tissues that support your teeth. A periodontal abscess is more common in adults and is caused by gum disease.
- The abscess's center liquefies and contains dead cells, germs, and other detritus. This region expands, causing tension beneath the skin and additional inflammation of the surrounding tissues. The pain is caused by pressure and inflammation.
- Certain abscesses are more common in those who have compromised immune systems.
- Those who have any of the following conditions are at risk of developing more serious abscesses. This is due to the body's diminished ability to fight infections.
Types of Abscess in Your Mouth
Oral abscesses can harm your teeth, gums, and throat. An abscess that occurs around a tooth is known as a tooth abscess (dental abscess).
There are several types of Abscesses:
1. Gingival Abscess:
A gingival abscess also called gum abscess is another name for a gingival abscess. This sort of abscess forms in the gums. It normally has little effect on your teeth.
2. Periapical Abscess
A periapical abscess is an infection that develops at the tip of the root of your tooth. This form of abscess can develop as a result of oral trauma or cavities.
3. Periodontal Abscess:
A periodontal abscess is a bacterial infection that affects the bones and tissues that support your teeth. It is frequently caused by periodontitis or gum disease.
4. Tonsil Abscess:
A tonsil abscess is a pus-filled pocket behind one of your tonsils. Tonsillar abscesses occur most frequently in teens and young adults.
5. Quinsy Abscess:
A Quinsy abscess is another name for a peritonsillar abscess. A quinsy is a pus deposit between your tonsils and the throat wall.
6. Retropharyngeal Abscess
A retropharyngeal abscess is a type of abscess that develops in the rear of your throat. When the lymph nodes in the back of your throat get infected, an abscess occurs.
Symptoms of Abscess
Symptoms of deeper skin abscesses or those inside your body are less visible. Some symptoms are related to the damaged bodily part.
You may encounter:
- Fatigue.
- Tenderness and pain.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Sensitive teeth.
- Having difficulty swallowing.
- You're having trouble opening your mouth.
- Sweating excessively.
- Appetite loss.
- Weight reduction.
Risk Factors of Mouth Abscess
These variables may raise your chances of developing a tooth abscess:
Inadequate dental habits and care. Not caring for your teeth and gums properly, such as brushing twice a day and flossing, might raise your risk of dental diseases. Tooth decay, gum disease, tooth abscess, and other dental and mouth issues are all possibilities.
A high-sugar diet. Sugary meals and beverages, such as sweets and sodas, can contribute to dental cavities and lead to tooth abscesses.
The mouth is parched. A dry mouth can raise your chances of developing tooth decay. Dry mouth is frequently caused by a side effect of some drugs or by ageing disorders.
Prevention of Mouth Abscess
Tooth decay must be avoided to avoid a tooth abscess.
To avoid tooth decay, take proper care of your teeth:
- Fluoride-containing water should be consumed.
- Brush your teeth for two minutes with fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day.
- Clean your teeth daily using dental floss or a water flosser.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or anytime the bristles get ragged.
- Consume healthful foods while limiting sugary foods and between-meal snacks.
- Check in with your dentist regularly for checkups and professional cleanings.
- Use an antiseptic or fluoride mouth rinse to give an extra layer of protection against tooth decay.
What is the Best Way to Treat an Abscess?
The treatment's goals are to remove the infection and prevent complications.
Treatment options for Mouth Abscesses include:
1. Incision and Drainage:
To drain the pus, your dentist makes a small incision (cut) in the abscess. A tiny rubber drain may also be installed. This keeps the region open, allowing the rest of the infection to drain.
2. Root Canal Treatment:
The root canal treatment (RCT) helps to remove the infection and save your tooth. This popular surgery removes the affected pulp from your tooth and fills the space with substance to avoid further infection.
The pulp is necessary while the tooth is growing, but once mature, the tooth may survive without it. Though your tooth should be returned to normal after the operation,
Your tooth should be restored to normal after the surgery, though you may require a dental crown to safeguard the root canal. If you take excellent care of your restored tooth, it can last a lifetime.
3. Tooth Extraction:
An abscessed tooth may become irreparably damaged. Your dentist may need to extract (pull) your tooth in certain instances.
4. Antibiotics:
Your dentist may advise you to take antibiotics as part of your treatment. While this treatment may help fight off leftover bacteria, it will not eliminate the source of the problem, which is the impacted tooth.
Can Abscess Heal on Its Own?
A dental abscess will not heal on its own. The pain may subside if an infection kills the pulp inside your tooth.
Because the nerve is no longer functioning, the pain stops, and you may not be able to feel it.
The bacteria, on the other hand, will continue to spread and kill surrounding tissue. Even if you are no longer in pain, consult the dentist near you if you have symptoms of a mouth abscess.
Conclusion
A dentist should treat an abscessed tooth. Even if the abscess has ruptured, you should have the area cleansed and inspected by your dentist to ensure the infection does not spread.
Remember to see your dentist regularly and don't put off frequent check-ups because prevention is vital.
These appointments let your dentist detect problems early on, when they may be easier to treat. If you're in pain, you should see your dentist right away to obtain the help you need.