Contents
- What is Oral Cavity Cancer?
- Oral Cavity Cancer Symptoms
- Oral Cavity Cancer Causes
- 1. Tobacco Use:
- 2. Alcohol Use:
- 3. Poor Nutrition:
- 4. A Weakened Immune System:
- 5. Age:
- 6. Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure:
- Oral Cavity Cancer Staging
- Oral Cavity And Pharynx Cancer
- Oral Cavity Cancer Treatment
- Oral Cavity Cancer Pictures
- The Way Forward: Oral Cavity Cancer Radiology
- Conclusion
Oral cavity cancer is a silent epidemic that affects numerous individuals around the world. Unfortunately, most people only realize their condition when it's too late to remedy it.
This means that awareness and understanding of its symptoms are crucial in effectively preventing and treating this disease.
In this blog post, we'll discuss everything you need to know about oral cavity cancer symptoms.
We aim to help people recognize the signs early so they can seek medical attention promptly, increasing their chances of survival.
So if you're curious or concerned about oral cavity cancers' unspoken epidemic, keep reading!
What is Oral Cavity Cancer?
Cancer of the Oral cavity is often referred to as the unspoken epidemic because it is one of the most prevalent, yet least discussed, cancers in America.
In fact, according to the American Cancer Society, nearly 53,000 people will be diagnosed with oral or oropharyngeal cancer this year.
While many cancers can be attributed to specific risk factors like smoking or excessive sun exposure, the cause of oral cavity cancer is not always clear.
The most common symptoms include a sore or lump in the mouth that doesn’t seem to go away, persistent bad breath, difficulty swallowing, numbness or pain in the face or neck, and loose teeth.
Other less common symptoms may include voice changes, facial swelling, and unexplained bleeding.
If you are experiencing any of these signs or symptoms, be sure to talk to your doctor as soon as possible.
Early detection is critical for the successful treatment of oral cavity cancer, so don’t delay in seeking medical attention if you have concerns about your health.
Oral Cavity Cancer Symptoms
Cancer of the oral cavity is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making it difficult to detect.
However, there are some signs and symptoms that may be indicative of oral cavity cancer. These include:
A sore or ulcer in the mouth that does not heal
Bleeding from the mouth
Persistent pain in the mouth
A lump or mass in the mouth
Voice changes
Difficulty swallowing
Weight loss
Early detection of oral cavity cancer is critical to successful treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, please see a doctor or dentist for evaluation.
Oral Cavity Cancer Causes
There are a variety of risk factors that can contribute to the development of oral cavity cancer, these include:
1. Tobacco Use:
Cigarette smoking, chewing tobacco, and more are some of the notorious reasons for Oral cancer. It is the most common cause of oral cavity cancer. Chewing tobacco and snuff are also risk factors.
Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes and using smokeless tobacco products increases your risk of developing oral cavity cancer. Tobacco use is responsible for approximately 75% of all oral cavity cancer cases.
2. Alcohol Use:
Drinking alcohol increases the risk of developing oral cavity cancer. This may not be common but it is one of the reasons for Oral cancer.
But, Drinking alcohol excessively can also increase your risk of developing oral cavity cancer.
3. Poor Nutrition:
A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of developing oral cavity cancer.
Human papillomavirus (HPV): HPV is a virus that is sexually transmitted and has been linked to an increased risk for certain types of oral cancer, including oral cavity cancer.
4. A Weakened Immune System:
People with HIV/AIDS and those undergoing radiation therapy or chemotherapy treatment for other cancers are at an increased risk of developing oral cavity cancer.
5. Age:
The risk of developing oral cavity cancer increases with age.
6. Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure:
Exposure to sunlight or other sources of ultraviolet radiation may increase the risk of developing oral cavity cancer.
Oral Cavity Cancer Staging
The staging of oral cavity cancer refers to how far the cancer has progressed.
There are four stages of oral cavity cancer, with stage I being the least severe and stage IV being the most severe.
The stages are determined by the size of the tumour and whether or not the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Stage 0: Abnormal cells are found in the inner lining of the oral cavity.
Stage I: The cancer is in one part of the oral cavity or tissue lining it. It may have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.
Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues and/or lymph nodes but not to any other parts of the body.
Stage III: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues and/or lymph nodes, as well as distant parts of the body such as lungs, bones, or other organs.
Stage IV: Cancer has spread throughout various organs, bones, and/or lymph nodes.
Once the stage of the cancer is determined, then a treatment plan can be created to best treat it.
Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of all three.
It’s important to seek the help of medical professionals to properly diagnose and stage oral cavity cancer.
This will allow them to create a personalized treatment plan that is tailored to your individual needs.
Oral Cavity And Pharynx Cancer
Oral cavity and pharynx cancer remains a significant health issue, despite a recent decline in its incidence. Globally, it ranks as the sixth most common cancer, and in the United States alone, around 35,000 people are expected to be diagnosed with this disease in 2020.
The majority of these cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, which develop from the thin, flat cells lining the mouth and throat. These cancers can affect various areas of the oral cavity and pharynx but are most commonly found in the tongue, gums, and the floor of the mouth. Less common types include adenocarcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphomas.
The primary risk factor for oral cavity and pharynx cancer is tobacco use, which includes cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and smokeless tobacco products like snuff and chewing tobacco. Alcohol consumption is another significant risk factor, and the combination of both tobacco and alcohol greatly increases the likelihood of developing this cancer.
Common symptoms of oral cavity and pharynx cancer include:
Persistent sores in the mouth
White or red patches on the gums, tongue, or mouth lining
Voice changes or hoarseness
Lumps or masses in the neck
Difficulty swallowing
Ear pain
Unexplained weight loss and fatigue
Early detection is crucial, as these cancers can be aggressive but are more treatable when diagnosed early. If any symptoms persist, seeking medical advice promptly is essential.
Oral Cavity Cancer Treatment
Cancer of the oral cavity is a relatively rare cancer, but it is on the rise.
According to the National Cancer Institute, the incidence of oral cavity cancer has increased by nearly two percent per year over the last decade.
oral cavity cancer can be difficult to detect in its early stages because it often does not produce any symptoms.
When symptoms do occur, they can be nonspecific and easily mistaken for other conditions.
That's why it's important to see your dentist or doctor for regular checkups so that any suspicious changes can be investigated.
If oral cavity cancer is diagnosed, treatment will depend on the stage of the disease.
Early-stage cancers may be treated with surgery, while more advanced cancers may require radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
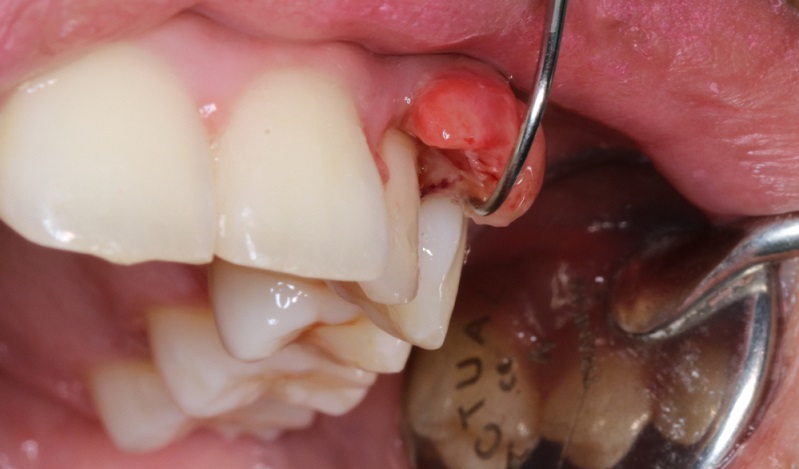
Oral Cavity Cancer Pictures
Oral cavity cancer, though less common than some other cancers, is a serious disease that can greatly affect your health. Early awareness of symptoms and risk factors is crucial for timely treatment.
The most common symptom is a sore or ulcer in the mouth that doesn’t heal, which can appear on the lips, gums, tongue, or inside the cheek. Other signs include mouth bleeding, loose teeth, voice changes, or difficulty swallowing.
Oral cancer risk factors include smoking, excessive alcohol use, betel nut chewing, and HPV infection. If you have any of these risks or experience persistent symptoms, consult a dentist or doctor promptly for evaluation. Early detection is key to successful treatment.
The Way Forward: Oral Cavity Cancer Radiology
Around 30% of new cancer cases and 70% of cancer deaths are linked to lifestyle and environmental factors. This highlights the importance of making healthy choices like maintaining a balanced diet, exercising, and avoiding tobacco to reduce cancer risk.
For oral cavity cancer, the key risk factors include tobacco use—such as cigarettes, cigars, and chewable tobacco—and excessive alcohol consumption, which increases the risk sixfold. A poor diet, especially one lacking in fruits and vegetables, also contributes to the risk, while antioxidants may offer some protection.
The most common type of oral cavity cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, originating in the flat cells lining the mouth. Other less common types include verrucous carcinoma, salivary gland tumors, and adenocarcinomas. Symptoms can vary but often include non-healing sores, changes in mouth color, difficulty swallowing, and unexplained bleeding.
Imaging tests, like CT and MRI scans, play a critical role in diagnosing and staging oral cavity cancer, helping determine the spread and guiding treatment plans. A biopsy may also be required for confirmation.
Ultimately, early detection and prevention are crucial. Understanding the risk factors and undergoing regular screenings can catch oral cavity cancer early, improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways: Preventing and Detecting Oral Cavity Cancer
- Early detection is critical: Catching oral cavity cancer early significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
- Recognize symptoms: Be proactive about seeking medical advice for any persistent sores, changes in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, or abnormal bleeding.
- Prevention strategies:
1. Avoid smoking and smokeless tobacco.
2. Limit alcohol consumption.
3. Practice good oral hygiene.
4. Reduce exposure to HPV and other risk factors.
5. Eat a diet rich in antioxidant-rich foods like fruits and vegetables.
- Screening: Individuals over 45 should have regular screenings by a knowledgeable physician to detect early signs of oral cancer.
- Awareness and action: Stay vigilant about any changes in your mouth and spread awareness to help combat this preventable disease.