Contents
- Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
- Root Causes of Periodontal Abscess
- What are the Complications of Periodontal Abscess?
- Diagnosis and Treatments for Periodontal Abscess
- Periodontal Abscess vs Periapical Abscess
- How to Prevent Periodontal Abscess?
- What is a Periodontal Abscess?
- Is Periodontal Abscess Painful?
- Can I Pop A Periodontal Abscess?
- How Long Does Periodontal Abscess Last?
- How To Treat Periodontal Abscess?
- Can Periodontal Abscess Heal On Its Own?
- Can Periodontal Abscess Be Treated With Antibiotics?
- What happens if I don't treat periodontal disease?
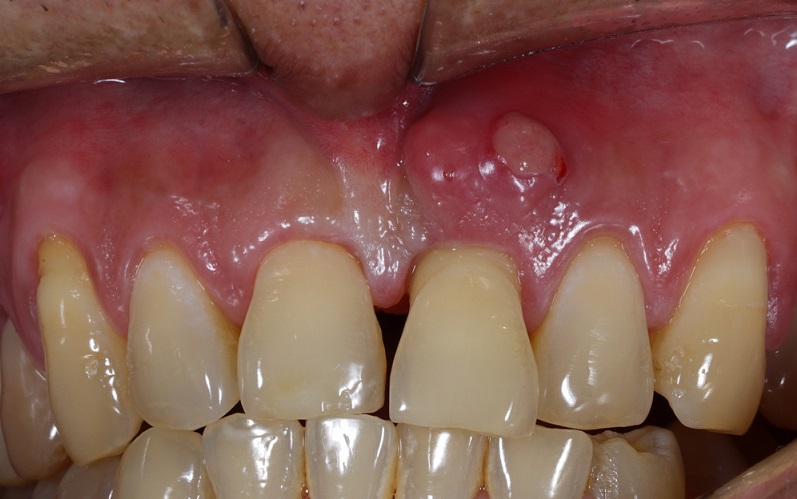
A periodontal abscess, often called a gum or tooth abscess, is a localized collection of pus within the gums or around the teeth.
Although anyone can develop a periodontal abscess, those who practice poor dental hygiene are more likely to obtain one.
If left untreated, an infection from a periodontal abscess can spread to other parts of your body and mouth, leading to more problems.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
So, how do you know if you’re dealing with a periodontal abscess? Well, your body has a way of sending out distress signals.
Keep an eye out for the following symptoms:
- A swollen bump on your gums (the most obvious)
- Pain or tenderness
- Toothache
- Swollen and red gums
- In some cases, you might notice pus oozing from the affected area or experience heightened sensitivity to hot or cold foods.
Root Causes of Periodontal Abscess
A periodontal abscess develops when oral bacteria get into the area between your teeth and gums.
The most frequent cause of this and the highest risk factor for periodontal abscesses is gum disease.
Additionally, you have the risk of getting a gum abscess if you have:
Bruxism (prolonged clenching and grinding of the teeth).
Teeth harmed by trauma or injury.
Restorations such as dental crowns, bridges, or fillings that are broken or damaged.
One of the main culprits for dental abscesses is poor oral hygiene.
When plaque builds up on your gums and teeth, it creates a cosy environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to infections that can escalate into abscesses.
A high-sugar diet- having sugar foods and drinks increases the risk of gum disease.
What are the Complications of Periodontal Abscess?
Untreated gum abscesses can result in several oral health problems, such as:
Degradation of the soft tissues and ligaments that surround your teeth.
Bone loss in the mandible.
Missing teeth.
It has been suggested by research that oral bacteria can spread to other areas of the body.
A periodontal abscess may occasionally be connected to:
Blood infection, or sepsis.
Heart inflammation.
Pneumonia
Brain swelling.
If you suspect a gum abscess, make an immediate appointment with a dentist. Timely intervention is essential to prevent problems.
Diagnosis and Treatments for Periodontal Abscess
Diagnosis for Periodontal Abscess
When diagnosing a gum abscess, a dentist will:
1. Studying your Symptoms
Your dentist will inquire about your symptoms, including the length of time the abscess has been there.
2. Taking a Periodontal Examination
They'll take measurements of the tooth's surrounding pockets. This lets them know how much if any, bone you've lost in the affected location.
3. Getting X-rays of the Teeth
An X-ray of the damaged tooth will be taken by your dentist.
This illustrates to them the extent of the infection and the severity of the abscess.
A periodontal abscess is a dental emergency that needs to be treated right away.
Treatment for Periodontal Abscesses
1. The Draining of Periodontal Abscesses
Your dentist might have to remove the abscess. Your gums will be lightly incised during this operation, and the infection will be drained by applying pressure.
2. Gum Disease Treatment
Your dentist may suggest scaling and root planing, deep cleaning of your teeth, or gum surgery to remove the infection.
3. Antibiotics
Your dentist may recommend an antibiotic course in addition to cleaning the affected region to lower your chance of reinfection.
4. Root Canal Therapy
You could require root canal therapy to preserve a tooth if a periodontal abscess spreads to it and becomes infected.
5. Removing Teeth
Your dentist might advise extracting an infected tooth in extreme circumstances.
Your dentist will discuss replacement choices with you if a tooth extraction is necessary.
A periodontal abscess is not something you can cure at home. Contact a dentist as soon as possible if you believe you have a gum abscess.
Periodontal Abscess vs Periapical Abscess
Periodontal Abscess
Origin: Periodontal abscess develops in the periodontium, the supporting structures around a tooth, including the gums and bone.
Cause: It typically results from untreated gum disease (periodontitis), where bacteria accumulate in the periodontal pockets formed between the teeth and gums.
Periapical Abscess
Origin: Periapical abscess begins within the tooth's pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels.
Cause: usually caused by untreated dental cavities or trauma that allows bacteria to invade the pulp chamber.
How to Prevent Periodontal Abscess?
Preventing periodontal abscesses starts with a commitment to good oral hygiene habits:
Brush your teeth twice daily using fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush.
Floss at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles between teeth.
Schedule regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings.
Address dry mouth concerns with your dentist to reduce your risk.
If you clench or grind your teeth, consider using a custom mouthguard to protect your gums and teeth.
By staying proactive and mindful of your oral health, you’re taking powerful steps towards preventing painful periodontal abscesses. With regular care and routine check-ups, you'll ensure a healthy, bright smile that lasts a lifetime.
Here’s to healthier gums and a confident, radiant smile!
What is a Periodontal Abscess?
It is a localized collection of pus in the gums or around teeth, often caused by bacterial infection. It can lead to swelling, pain and other health issues.
Is Periodontal Abscess Painful?
Absolutely. Periodontal abscesses typically cause throbbing pain, making it essential to seek timely dental intervention for relief.
Can I Pop A Periodontal Abscess?
No. it is strongly advised against popping an abscess. This should be addressed by a dental professional to avoid complications and ensure proper treatment.
How Long Does Periodontal Abscess Last?
The duration varies but prompt treatment can shorten the healing process. Seeking dental care is crucial for a timely resolution.
How To Treat Periodontal Abscess?
Treatment involves draining the abscess and addressing the underlying infection. Antibiotics can be prescribed, and dental procedures may be required for severe cases.
Can Periodontal Abscess Heal On Its Own?
Generally, it is unlikely.
Can Periodontal Abscess Be Treated With Antibiotics?
Yes. antibiotics are often prescribed to combat the bacterial infection. However, they are typically part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include dental procedures.
What happens if I don't treat periodontal disease?
It can lead to severe consequences, including tooth loss, bone damage, and systemic health issues. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent these complications and maintain over well-being.