Contents
- What is Tooth Enamel Erosion?
- What are the Symptoms of Enamel Erosion?
- What Does Tooth Erosion Feel Like?
- What are the Causes of Enamel Erosion?
- 1. Acidic foods and drinks:
- 2. GI disorders and acid reflux:
- 3. Dry mouth:
- 4. Brushing Style:
- 5. Certain medications:
- 6. Environmental Factors:
- Can Tooth Erosion Go Away on Its Own?
- Diagnosis for Tooth Erosion
- Treatment Options to Restore Tooth Enamel
- How to Prevent Dental Erosion at Home?
- Conclusion
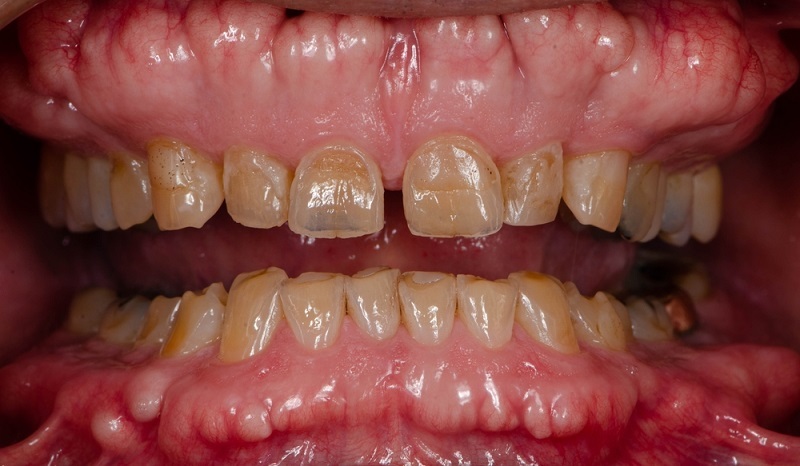
Preserving a healthy and bright smile demands caring for our teeth, particularly the outer, protective coating known as dental enamel.
The causes, signs, and probable restoration procedures of dental enamel erosion will all be covered in this blog.
So let's begin the process of protecting your priceless enamel and making sure you have a stunning, healthy smile for years to come.
What is Tooth Enamel Erosion?
Imagine your teeth as strong soldiers who are standing guard, protecting the delicate inner layers. Tooth enamel, the hard outer layer, is their protective armor.
Enamel is even stronger than bone and shields the sensitive dentin and pulp from harm.
But, just like armor can suffer wear and tear over time, tooth enamel can erode, leaving our teeth vulnerable to various dental issues.
Dental erosion happens when acids dissolve away a portion of your teeth's enamel surface.
Acidic foods, beverages, medications, frequent vomiting, or acid reflux are the usual culprits. Erosion differs from tooth decay in that microorganisms do not bring it on.
What are the Symptoms of Enamel Erosion?
While the body can heal and repair itself, enamel regrettably cannot. Sadly, when tooth enamel is damaged by acid, sugar, stress, and other circumstances.
Since enamel doesn’t contain living cells, it can’t heal like a broken bone. If you're concerned about enamel erosion, watch for these symptoms:
Discoloration: Yellowing of the teeth.
Tooth Sensitivity: Pain or discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks.
Cracks and Chips: Visible damage on the tooth surface.
Tooth Indentations: Small depressions or "cupping" on the biting surface.
Cavities and Tooth Decay: The erosion of enamel makes teeth more vulnerable to cavities.
As enamel erodes, teeth lose their protective layer, exposing them to bacteria and increasing the risk of cavities. Untreated cavities can damage the tooth's nerve fibers, potentially leading to infection, abscesses, and a weakened immune system.
Cavities can develop to the enamel corroding and eroding.
Cavities are a type of tooth decay, so when the enamel on our teeth begins to erode, the absence of a protective layer leaves our teeth exposed and susceptible to oral germs.
Untreated cavities and dental decay impair the tooth's delicate nerve fibres, leading to an infection or abscess and making us ill because our immune systems are weakened.
What Does Tooth Erosion Feel Like?
A permanent or irreversible loss of enamel from the tooth surface is referred to as tooth erosion.
It results in uneven, jagged, or rough tooth edges and may cause the following symptoms:
Pain or sensitivity: Drinking hot, cold, or sweet liquids can cause intense pain or sensitivity.
Discoloration of the teeth: When enamel is lost, dentin is exposed, giving teeth a yellowish hue.
Cavity: Cavities are more likely to occur when there is a loss of enamel.
Abscess and tooth loss: Though rare, extreme occurrences of enamel loss might lead to an abscess or tooth loss.
What are the Causes of Enamel Erosion?
Several variables, such as the following, can contribute to enamel erosion:
1. Acidic foods and drinks:
If ingested in excess, citrus fruits, soda, sports drinks, and wine are just a few examples of acidic foods and drinks that can erode enamel.
2. GI disorders and acid reflux:
Enamel degradation can result from repeated exposure to stomach acid.
3. Dry mouth:
Saliva protects enamel by balancing acids. Enamel erosion is more likely to occur if there is insufficient saliva.
4. Brushing Style:
Brushing too vigorously might gradually wear down enamel if done with a hard-bristled toothbrush.
5. Certain medications:
These include
Chewable vitamin C tablets
Liquid iron supplements
Cough suppressants
Mouth rinses
Chemotherapy or other drugs that irritate the stomach
Asthma medication from puffers
6. Environmental Factors:
These include elements that contribute to the mechanical wearing away of the tooth, such as friction, stress, corrosion, wear and tear, etc.
Can Tooth Erosion Go Away on Its Own?
Tooth erosion is an irreversible condition. It involves the erosion of enamel brought on by the chemical reaction of acids found in some foods.
The edges of the teeth take on a rough, crooked, and jagged appearance as a result of the enamel breaking or chipping off.
Cavities may arise as a result of it. These are the structural alterations to the teeth that are irreversible and permanent.
Certain techniques, such as dental veneers, crowns, and restorations or fillings, can only repair the damage.
Diagnosis for Tooth Erosion
Under the direction of a dentist, a proper treatment plan is followed by the diagnosis of tooth erosion.
There are crucial steps in it, including:
Inquiring about the main complaints: The patient is questioned about the sensitivity and soreness of their teeth. This entails finding out when and how both symptoms first appeared.
Mouth examination: For a correct diagnosis, a thorough examination of the mouth cavity is required.
Dental instruments are used to probe teeth in this step to look for cavities.
Dental X-rays are analyzed as part of the radiographic examination to determine the degree of tooth decay or cavities.
Treatment Options to Restore Tooth Enamel
If enamel erosion has started, your dentist may suggest the following treatments:
Dental Bonding: A tooth-coloured resin is applied to cover and protect mildly eroded teeth, preventing further damage and staining.
Dental Veneers: For more severe cases, thin veneers are custom-made and cemented to the teeth to restore appearance and function.
- Dental Crowns: In extreme situations, a dental crown may be needed to protect the remaining enamel and restore the tooth's strength.
How to Prevent Dental Erosion at Home?
Reduce your consumption of fruit juices, sports drinks, soft drinks, and diet beverages.
Eat fewer acidic food items.
After consuming acidic foods, in between meals, and after consuming tea or coffee, drink water.
After vomiting, rinse your mouth with milk or water.
20 minutes after consuming acidic foods, chew sugar-free gum to stimulate salivation.
To prevent acid reflux, avoid alcohol, and fast for three hours before going to bed.
Frequent dental and oral health examinations.
Conclusion
You can preserve the strength of your enamel and keep your teeth healthy by being aware of the causes and symptoms of enamel erosion and implementing preventative steps.
In circumstances where enamel erosion has taken place, restoration procedures and artificial enamel substitutes present potential ways to keep your gorgeous smile.
To guarantee that your teeth stay strong and brilliant for a lifetime, adopt good dental hygiene practices, make decisions that are kind to your enamel, and schedule frequent checkups with your dentist.
Do not forget that a little kindness today can result in a lifetime of smiles tomorrow.